Bought By: 8234
Rating: 4.9


Bachelor of Arts (Honours) Economics (BAECH) comes in the category of Core Courses (CC) offered by IGNOU. In semester-I, BECC–101, students get introduced to important principles of microeconomics. The topics covered in this course include demand and supply, consumer behaviour, cost of production, monopoly and oligopoly, factor, land and labour markets, welfare, market failure, and government’s role.
Get Good Marks in your BAECH Economics Programme in the Term-End Exams even if you are busy in your job or profession.
We've sold over 39,648,497 Help Books and Delivered 48,262,259 Assignments Since 2002.
As our customers will tell you...yes, it really result-oriented.
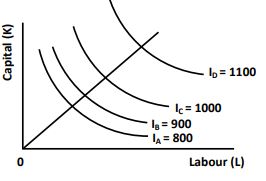 (i) Identify the returns to scale represented by the above set of isoquants. What are the factors that lead to such returns to scale?
(ii) Expansion of output by a firm comes with increasing average unit cost of production. Identify the phenomenon in terms of scale economies. Also discuss the reasons behind such a phenomenon.
(b) What are the reasons behind internal economies and internal diseconomies of scale faced by a firm?
2. a) Using appropriate diagrams compare and contrast long-run equilibrium conditions faced by a firm under perfect and monopolistic competition market structures.
(b) A firm operating in a competitive market faces a marginal cost function given by
MC(Q) = 2Q + 100
where MCis the marginal cost, Q represents level of output produced and P is the price. If the unit price of output is Rs 60, what level of output will maximize profits? What will be the maximum profit? At what minimum price will the firm produce a positive output?
Assignment Two
Answer the following Middle Category questions in about 250 words each. Word limit does not apply in application part of the question.
3 (a) Illustrate with the help of a diagram, higher the price elasticity of demand, larger will be the per unit tax burden borne by the producers.
(b) Using appropriate diagrams, compare and contrast the shapes of demand and supply curves when there are multiple equilibriums with the shapes of demand and supply curves when there is a unique equilibrium with respect to a commodity.
4. Explain the concept of Technical efficiency. Technical efficiency will not necessarily ensure overall Pareto optimum product mix. Why?
5. With the help of a diagram, illustrate the deadweight loss associated with a negative externality. How does a Pigouvian tax work to solve the welfare loss from such a deadweight loss?
Assignment Three
Answer the following Short Category questions in about 100 words each. Word limit does not apply in application part of the question.
6. Why does the marginal rate of technical substitution (MRTS) decline as we move rightward and downward along a convex-shaped isoquant?
7. The concept of quasi-rent is an extension of the Ricardian concept of rent to other factors of production. Elucidate.
8. The concept of quasi-rent is an extension of the Ricardian concept of rent to other factors of production. Elucidate.
9. Discuss the concept of excess capacity associated with the long run equilibrium under Monopolistic competition.
10. Draw an income consumption curve in case the good marked on the horizontal axis is a necessity good while that marked on the vertical axis is a superior good.
(i) Identify the returns to scale represented by the above set of isoquants. What are the factors that lead to such returns to scale?
(ii) Expansion of output by a firm comes with increasing average unit cost of production. Identify the phenomenon in terms of scale economies. Also discuss the reasons behind such a phenomenon.
(b) What are the reasons behind internal economies and internal diseconomies of scale faced by a firm?
2. a) Using appropriate diagrams compare and contrast long-run equilibrium conditions faced by a firm under perfect and monopolistic competition market structures.
(b) A firm operating in a competitive market faces a marginal cost function given by
MC(Q) = 2Q + 100
where MCis the marginal cost, Q represents level of output produced and P is the price. If the unit price of output is Rs 60, what level of output will maximize profits? What will be the maximum profit? At what minimum price will the firm produce a positive output?
Assignment Two
Answer the following Middle Category questions in about 250 words each. Word limit does not apply in application part of the question.
3 (a) Illustrate with the help of a diagram, higher the price elasticity of demand, larger will be the per unit tax burden borne by the producers.
(b) Using appropriate diagrams, compare and contrast the shapes of demand and supply curves when there are multiple equilibriums with the shapes of demand and supply curves when there is a unique equilibrium with respect to a commodity.
4. Explain the concept of Technical efficiency. Technical efficiency will not necessarily ensure overall Pareto optimum product mix. Why?
5. With the help of a diagram, illustrate the deadweight loss associated with a negative externality. How does a Pigouvian tax work to solve the welfare loss from such a deadweight loss?
Assignment Three
Answer the following Short Category questions in about 100 words each. Word limit does not apply in application part of the question.
6. Why does the marginal rate of technical substitution (MRTS) decline as we move rightward and downward along a convex-shaped isoquant?
7. The concept of quasi-rent is an extension of the Ricardian concept of rent to other factors of production. Elucidate.
8. The concept of quasi-rent is an extension of the Ricardian concept of rent to other factors of production. Elucidate.
9. Discuss the concept of excess capacity associated with the long run equilibrium under Monopolistic competition.
10. Draw an income consumption curve in case the good marked on the horizontal axis is a necessity good while that marked on the vertical axis is a superior good.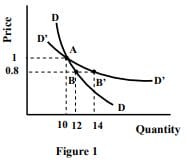 Assignment Two
3. (a) Given that a firm experiences a linear homogenous production function, comment upon the shape of the Expansion path, both in the long run and in the short run.
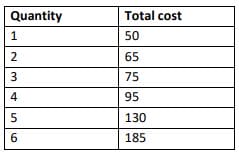
(b) Consider the following Table which gives total cost schedule of a firm. Given that the average fixed cost of producing 2 units of output is Rs. 10. Find the total variable cost, total fixed cost, average variable cost, average fixed cost, short-run average cost, and short-run marginal cost schedules of the firm for the corresponding values of output.
Assignment Two
3. (a) Given that a firm experiences a linear homogenous production function, comment upon the shape of the Expansion path, both in the long run and in the short run.
(b) Consider the following Table which gives total cost schedule of a firm. Given that the average fixed cost of producing 2 units of output is Rs. 10. Find the total variable cost, total fixed cost, average variable cost, average fixed cost, short-run average cost, and short-run marginal cost schedules of the firm for the corresponding values of output.
 4. (a) Draw a kinked demand curve and explain how a change in marginal costs may not affect the price in the market.
(b) A Monopoly faces market demand given by Q = 30 – P, where Q stands for quantity and P for price. Total cost function is given by C(Q) = 2Q2. Find the profit maximizing price and quantity and the resulting profit to the monopoly. Compare your results with the equilibrium quantity and price of that of a perfect competitive industry.
5. (a) With the help of a diagram show the effect of the minimum wage rule on the labour market given that the wage is set above the market equilibrium wage rate.
(b) What will be the resultant effects on the labour market if the minimum wage is set below the market equilibrium wage rate?
Assignment Three
6. Discuss the types of non-cooperative behaviour under Oligopoly
7. Law of Diminishing returns applies only in the short-run. Do you agree?
8. Illustrate the relation between the Value of Marginal product and Marginal Revenue product of a factor under perfect competition.
9. Discuss the central problems of an Economy.
10. Illustrate with the help of a diagram, higher the price elasticity of supply, larger will be the per unit tax burden borne by the consumers.
4. (a) Draw a kinked demand curve and explain how a change in marginal costs may not affect the price in the market.
(b) A Monopoly faces market demand given by Q = 30 – P, where Q stands for quantity and P for price. Total cost function is given by C(Q) = 2Q2. Find the profit maximizing price and quantity and the resulting profit to the monopoly. Compare your results with the equilibrium quantity and price of that of a perfect competitive industry.
5. (a) With the help of a diagram show the effect of the minimum wage rule on the labour market given that the wage is set above the market equilibrium wage rate.
(b) What will be the resultant effects on the labour market if the minimum wage is set below the market equilibrium wage rate?
Assignment Three
6. Discuss the types of non-cooperative behaviour under Oligopoly
7. Law of Diminishing returns applies only in the short-run. Do you agree?
8. Illustrate the relation between the Value of Marginal product and Marginal Revenue product of a factor under perfect competition.
9. Discuss the central problems of an Economy.
10. Illustrate with the help of a diagram, higher the price elasticity of supply, larger will be the per unit tax burden borne by the consumers.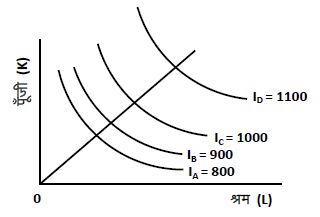 i) उपर्युक्त समोत्पाद वक्रों द्वारा प्रदर्शित पैमाने की प्रतिफल अवस्था को बताइये। कौन-से कारक प्रतिफल अवस्थाओं के लिए उत्तरदायी हैं।
ii) किसी फर्म द्वारा उत्पादन का विस्तार प्रति इकाई बढ़ती हुई औसत लागत के साथ होता है। इस विचार को मितव्ययताओं के पैमाने के रूप में व्यक्त करें। इस विचार के पीछे के कारणों को भी बतायें।
iii) किसी फर्म द्वारा सामना की जाने वाली आंतरिक मितव्ययताओं एवं बाह्य मितव्ययताओं के पीछे कारणों को बताएं।
2) क) उपयुक्त रेखाचित्र का प्रयोग कर पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता एवं एकाधिकारात्मक प्रतियोगिता बाज़ार के अंतर्गत किसी फर्म द्वारा दीर्घकालीन संतुलन के प्राप्ति हेतु पूरी की जाने वाली शर्तों के बीच तुलना करें।
ख) पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता वाले बाज़ार के अंतर्गत कार्यशील एक फर्म का सीमांत लागत फलन इस प्रकार है -
MC (Q) = 2Q + 100
जिसमें सीमांत लागत MC है, Q उत्पादन की मात्रा है तथा P कीमत है। यदि उत्पादन की प्रति इकाई कीमत रु.60 है तो उत्पादन के किस स्तर पर लाभ अधिकतम होगा ? अधिकतम लाभ क्या होगा? किस न्यूनतम कीमत पर फर्म धनात्मक उत्पादन करेगी?
सत्रीय कार्य-2
निम्नलिखित मध्यम उत्तरीय प्रश्नों का उत्तर लगभग 250 शब्दों में दें।
3. क) रेखाचित्र की सहायता से यह प्रदर्शित करें कि माँग की कीमत लोच जितनी अधिक होगी, उतना ही अधिक कर का भार उत्पादक द्वारा वहन किया जाएगा।
ख) उपयुक्त रेखाचित्र का प्रयोग कर बहु संतुलन स्तर के तहत् माँग एवं पूर्ति की आकृतियों की तुलना एक अद्वितीय संतुलन स्तर के तहत माँग एवं पूर्ति की आकृतियों से कीजिए।
4) तकनीकी दक्षता की अवधारणा की व्याख्या करें। यह आवश्यक नहीं कि तकनीकी दक्षता कुल- मिलाकर परेटो अनुकूलतम उत्पाद मिश्र को सुनिश्चित करें। इसके कारण बताएं ।
5) रेखाचित्र की सहायता से नकारात्मक बाह्यताओं से जुड़ी मृत भार घाटे (deadweight loss ) का प्रदर्श करें। इस प्रकार मृत भार घाटे की हानि से किस प्रकार पीगूवीयन (Pigouvian) कर समाधान प्रस्तुत करता है?
सत्रीय कार्य-3
निम्नलिखित लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्नों का उत्तर लगभग 100 शब्दों में दें।
6. जब हम किसी उन्नतोदर (convex) समोत्पाद वक्र पर अपर तथा नीचे की ओर गमन करते हैं। तब तकनीकी सीमांत स्थानपित्त दर (MRTS) क्यों घटती है ?
7. 'उपभोक्ता की बचत की अवधारणा ह्रासमान सीमांत उपयोगिता के नियम से व्युत्पन्न की जाती है - व्याख्या करें।
8. अंतर्पण्य (Arbitrage) से आप क्या समझते हैं ?
9. आभासी लगान की अवधारणा अन्य उत्पत्ति के साधनों के लिए रिकार्डियन (Ricardian) लगान की अवधारणा का ही विस्तार है। विवेचना करें।
10. एकाधिकारात्मक प्रतियोगिता के तहत् दीर्घकालीन संतुलन से जुड़ी अतिरेक क्षमता की अवधारणा की चर्चा कीजिए ।
i) उपर्युक्त समोत्पाद वक्रों द्वारा प्रदर्शित पैमाने की प्रतिफल अवस्था को बताइये। कौन-से कारक प्रतिफल अवस्थाओं के लिए उत्तरदायी हैं।
ii) किसी फर्म द्वारा उत्पादन का विस्तार प्रति इकाई बढ़ती हुई औसत लागत के साथ होता है। इस विचार को मितव्ययताओं के पैमाने के रूप में व्यक्त करें। इस विचार के पीछे के कारणों को भी बतायें।
iii) किसी फर्म द्वारा सामना की जाने वाली आंतरिक मितव्ययताओं एवं बाह्य मितव्ययताओं के पीछे कारणों को बताएं।
2) क) उपयुक्त रेखाचित्र का प्रयोग कर पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता एवं एकाधिकारात्मक प्रतियोगिता बाज़ार के अंतर्गत किसी फर्म द्वारा दीर्घकालीन संतुलन के प्राप्ति हेतु पूरी की जाने वाली शर्तों के बीच तुलना करें।
ख) पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता वाले बाज़ार के अंतर्गत कार्यशील एक फर्म का सीमांत लागत फलन इस प्रकार है -
MC (Q) = 2Q + 100
जिसमें सीमांत लागत MC है, Q उत्पादन की मात्रा है तथा P कीमत है। यदि उत्पादन की प्रति इकाई कीमत रु.60 है तो उत्पादन के किस स्तर पर लाभ अधिकतम होगा ? अधिकतम लाभ क्या होगा? किस न्यूनतम कीमत पर फर्म धनात्मक उत्पादन करेगी?
सत्रीय कार्य-2
निम्नलिखित मध्यम उत्तरीय प्रश्नों का उत्तर लगभग 250 शब्दों में दें।
3. क) रेखाचित्र की सहायता से यह प्रदर्शित करें कि माँग की कीमत लोच जितनी अधिक होगी, उतना ही अधिक कर का भार उत्पादक द्वारा वहन किया जाएगा।
ख) उपयुक्त रेखाचित्र का प्रयोग कर बहु संतुलन स्तर के तहत् माँग एवं पूर्ति की आकृतियों की तुलना एक अद्वितीय संतुलन स्तर के तहत माँग एवं पूर्ति की आकृतियों से कीजिए।
4) तकनीकी दक्षता की अवधारणा की व्याख्या करें। यह आवश्यक नहीं कि तकनीकी दक्षता कुल- मिलाकर परेटो अनुकूलतम उत्पाद मिश्र को सुनिश्चित करें। इसके कारण बताएं ।
5) रेखाचित्र की सहायता से नकारात्मक बाह्यताओं से जुड़ी मृत भार घाटे (deadweight loss ) का प्रदर्श करें। इस प्रकार मृत भार घाटे की हानि से किस प्रकार पीगूवीयन (Pigouvian) कर समाधान प्रस्तुत करता है?
सत्रीय कार्य-3
निम्नलिखित लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्नों का उत्तर लगभग 100 शब्दों में दें।
6. जब हम किसी उन्नतोदर (convex) समोत्पाद वक्र पर अपर तथा नीचे की ओर गमन करते हैं। तब तकनीकी सीमांत स्थानपित्त दर (MRTS) क्यों घटती है ?
7. 'उपभोक्ता की बचत की अवधारणा ह्रासमान सीमांत उपयोगिता के नियम से व्युत्पन्न की जाती है - व्याख्या करें।
8. अंतर्पण्य (Arbitrage) से आप क्या समझते हैं ?
9. आभासी लगान की अवधारणा अन्य उत्पत्ति के साधनों के लिए रिकार्डियन (Ricardian) लगान की अवधारणा का ही विस्तार है। विवेचना करें।
10. एकाधिकारात्मक प्रतियोगिता के तहत् दीर्घकालीन संतुलन से जुड़ी अतिरेक क्षमता की अवधारणा की चर्चा कीजिए ।To attend IGNOU BECC-101 Term-End Examination, you must first submit your Assignments to the university and it is possible from the BECC-101 study material. You can solve all necessary Assignments using Help Books. This will help in gaining good marks.
All best wishes with our efforts that you do not meet any obstacle before attending examinations next year. You can pass the BAECH Economics Programme Annual Exams with a good grade using Books/Materials from any one place at home or anywhere else!
ALL THE BEST!!!
Team GullyBaba