IGNOU MEC-01/MEC-101 (July 2024 - January 2025) Assignment Questions
SECTION A
Answer the following questions in about 700 words each. The word limits do not apply in case of numerical questions.
1. a. The production function of a small factory that produces and sells toys is:
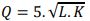
Where Q is the number of toys produced each day, L is the labour hours and k is the machine hours. Suppose 9 labour hours and 9 machine hours are used every day, what is the maximum number of toys that can be produced in a day? Calculate the marginal product of labour when 9 labour hours are used each day together with 9 machine hours.
Suppose the firm doubles both the amount of labour and machine hours used per day. Calculate the increase in output. Comment on the returns to scale in the operation
b. Define the term ‘Shepard’s lemma’. Assume that the production function of a producer is given by Q=5L0.5 K 0.3, where Q,L and K denote output, labour and capital respectively. If labour cost ₹ 1 per unit and capital ₹2, find the least cost combination of inputs (L&K)
2. Consider a Cobb-Douglas utility function
U (X, Y) = Xα Y (1- α),
Where X and y are the two goods that a consumer consumes at per unit prices of Px and Py respectively. Assuming the income of the consumer to be ₹M, determine:
a. Marshallian demand function for goods X and Y.
b. Indirect utility function for such a consumer.
c. The maximum utility attained by the consumer where α =1/2, Px =₹ 2, Py = ₹ 8 and M= ₹ 4000.
d. Derive Roy’s identity
SECTION B
Answer the following questions in about 400 words each.
3. a.) What do you mean by market failure? What are its causes?
b) What are the two principles of justice as mentioned by the philosopher Rawls?
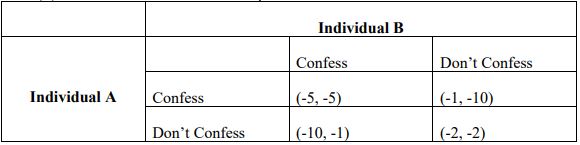
4. a.) Define games of complete and incomplete information
b.) From the following pay-off matrix, where the payoffs (the negative values) are the years of possible imprisonment for individuals A and B, determine:
(i) The optimal strategy for each individual.
(ii) Do individuals A and B face a prisoner’s dilemma?
5. a) What are the conditions of Pareto optimality?
b) Suppose an investor is concerned about a business choice in which there are three prospects. The probability and returns are given below:
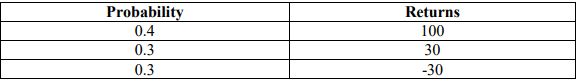
What is the expected value of the uncertain investment? What is the variance?
6. a.) Do you agree that by paying higher than the minimum wage, employers can retain skilled workers, increase productivity, or ensure loyalty? Comment on the statement in the light of efficiency wage model.
b.) There are two firms 1 and 2 in an industry, each producing output Q1 and Q2 respectively and facing the industry demand given by P=50-2Q, where P is the market price and Q represents the total industry output, that is Q= Q1 + Q2. Assume that the cost function is C = 10 + 2q. Solve for the Cournot equilibrium in such an industry.
7. Write short notes on following:
a) vNM expected utility theory
b) Slutsky’s theorem
c) Arrow prat measure of risk averseness
d) Bergson-Samuelson Social welfare function
IGNOU MEC-01/MEC-101 (July 2023 - January 2024) Assignment Questions
SECTION A
Answer the following questions in about 700 words each.
1. a. A monopolist uses one input X, which she purchases at the fixed price p=5 in order to produce output q. Her demand and production functions are:
P=85-3q and q= 2x 1/2 respectively.
Derive the equilibrium output and equilibrium profit.
b. “In real world, sometimes it is not possible to achieve optimum welfare.” Comment and discuss the obstacles in attaining Pareto optimum.
2. Given a Cobb-Douglas utility function
U (X, Y) = X 1/2 Y 1/2,
Where X and y are the two goods that a consumer consumes at per unit prices of Px and Py respectively. Assuming the income of the consumer to be ₹M, determine:
a. Marshallian demand function for goods X and Y.
b. Indirect utility function for such a consumer.
c. The maximum utility attained by the consumer where α =1/2, Px =₹ 2, Py= ₹ 8 and M= ₹ 4000.
d. Derive Roy’s identity.
SECTION B
Answer the following questions in about 400 words each.
3. a.) How is Cournot’s model of oligopoly different from Bertrand’s model of oligopoly?
b.) Suppose the demand for a product is given by p=d (q)=−0.8q+150 and the supply for the same product is given by p=s(q)=5.2q
For both functions, q is the quantity and p is the price. Find out producer surplus and consumer surplus.
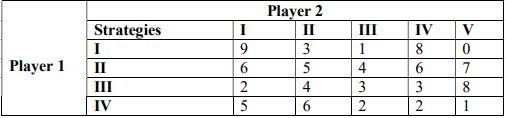
4. a.) Differentiate between Cooperative and non-cooperative game theory.
b.) From the following pay-off matrix, determine:
(i) The optimal strategy for each individual.
(ii) Value of the game.
5. a.) Do you agree that by paying higher than the minimum wage, employers can retain skilled workers, increase productivity, or ensure loyalty? Comment on the statement in the light of efficiency wage model.
b.) There are two firms 1 and 2 in an industry, each producing output Q1 and Q2 respectively and facing the industry demand given by P=50-2Q, where P is the market price and Q represents the total industry output, that is Q= Q1 + Q2. Assume that the cost function is C = 10 + 2q. Solve for the Cournot equilibrium in such an industry.
6. a.) Do you think that a risk-averse individual gamble or will a risk lover purchase insurance? Explain your answer.
b) Radha has assets worth 10,000 rupees and is facing a loss of 3,600 with a probability of 0.002. She is indifferent between paying G rupees for insurance protection and assuming the risk of loss personally. She values total assets of amount w≥0 according to the utility function u (w) = w1/2. Determine G.
7. Write short notes on following:
a) Different types of price discrimination
b) Bilateral monopoly
c) Economies of Scale
d) Pooling and separating equilibrium
Buy MEC-01/MEC-101 Assignment IGNOU MEC-01/MEC-101 (July 2024 - January 2025) Assignment Questions
खंड - क
प्रत्येक प्रश्न का उत्तर लगभग 700 शब्दों में देना है। संख्यात्मक प्रश्नों पर शब्द सीमा लागू नहीं होती।
1. (क) खिलौनों का उत्पादन और बिक्री करने वाले एक छोटे कारखाने का उत्पादन फलन है:
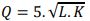
जहाँ Q प्रत्येक दिन उत्पादित खिलौनों की संख्या है L श्रम घंटे है और K मशीन घंटे है। मान लीजिए कि हर दिन 9 श्रम घंटे और 9 मशीन घंटे का उपयोग किया जाता है, तो एक दिन में अधिकतम कितने खिलौने बनाए जा सकते हैं? श्रम के सीमांत उत्पाद की गणना करें जब 9 मशीन घंटे के साथ प्रत्येक दिन 9 घंटे का उपयोग किया जाता है।
मान लीजिए कि फर्म प्रतिदिन उपयोग किए जाने वाले श्रम और मशीनी घंटों दोनों की मात्रा दो गुणा कर देती है। उत्पादन में वृद्धि की गणना कीजिए इस संचालन में पैमाने के प्रतिफल पर टिप्पणी कीजिए ।
(ख) शेपर्ड गृहीत पद को परिभाषित कीजिए। मान लीजिए कि किसी उत्पादक का उत्पादन Q-5L0.5K0.3 दिया गया है, जहाँ QL और K क्रमशः उत्पादन, श्रम तथा पूँजी को निरूपित करते हैं। यदि श्रम लागत ₹1 प्रति इकाई और पूँजी ₹2 है, तो साधनों (LK) के न्यूनतम लागत संयोजन ज्ञात कीजिए ।
2. निम्नलिखित कॉब-डगलस उपयोगिता फलन पर विचार कीजिए:
U(x,y)= 𝑿 𝜶𝒀 (𝟏−𝜶)
जहाँ X और Y दो वस्तुएँ हैं जिनका उपभोग उपभोक्ता क्रमश: P और Py की प्रति इकाई कीमतों पर करता है। उपभोक्ता की आय ₹M मानते हुए निर्धारित कीजिए:
(क) वस्तुओं x और y के लिए मार्शलीय माँग फलन
(ख) उपभोक्ता का अप्रत्यक्ष उपयोगिता फलन
(ग) उपभोक्ता द्वारा प्राप्त अधिकतम उपयोगिता जहां = P = ₹2, P = ₹8 और M=₹4000 है।
(घ) रॉय की सर्वसमिका (Identity ) की व्युत्पत्ति कीजिए।
खंड — ख
प्रत्येक प्रश्न का उत्तर लगभग 500 शब्दों में देना है। परिमाणात्मक प्रश्नों पर शब्द सीमा लागू नहीं होती।
3. (क) बाज़ार विफलता से आपका क्या तात्पर्य हैं? इसके कारण क्या हैं?
(ख) दार्शनिक रॉल्स द्वारा वर्णित न्याय के दो सिद्धांत क्या हैं?
4. (क) संपूर्ण और अपूर्ण सूचना द्युतों को परिभाषित करें।
(ख) इस प्रतिप्राप्ति आव्यूह पर विचार कीजिए: ऋणात्मक संख्याएँ दो व्यक्तियों A और B के संभावी कारावास में है।
(i) दोनों के लिए अभीष्ट युक्तियाँ निर्धारित कीजिए ।
(ii) क्या A तथा B व्यक्ति के समक्ष बंदी की दुविधा उपस्थित है?

5. (क) पेरोटो इष्टतम की शर्तें क्या हैं?
(ख) माना कि एक निवेशकर्त्ता एक व्यवसाय विकल्प के बारे में चिंतित है, जिसमें तीन संभावनाएँ हैं, प्रायिकता तथा प्रतिफल नीचे दिए गए है:

अनिश्चित निवेश का प्रत्याशित मान क्या है? विचरण क्या है?
6. (क) क्या आप सहमत हैं कि न्यूनतम वेतन से अधिक भुगतान करके नियोक्ता कुशल श्रमिकों को बनाए रख सकते हैं, उत्पादकता बढ़ा सकते हैं, या वफादारी सुनिश्चित कर सकते हैं? दक्षता मजदूरी मॉडल के आलोक में कथन पर टिप्पणी कीजिए ।
(ख) एक उद्योग में दो फर्म 1 और 2 हैं, जिनमें से प्रत्येक क्रमशः Q और Q2 आउटपुट का उत्पादन करती है और P= 50-2Q द्वारा दी गई उद्योग मांग का सामना करती है, जहाँ P बाजार मूल्य है और Q कुल उद्योग आउटपुट का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है, जो Q=Q1 + Q2 है। मान लें कि लागत फलन C=10=2q है। ऐसे उद्योग में कूर्नो संतुलन के लिए हल करें।
7. निम्नलिखित पर संक्षिप्त टिप्पणीयाँ लिखिए:
(क) VNM प्रत्याक्षित सिद्धांत
(ख) स्लटस्की प्रमेय
(ग) जोखिम विरति का ऐरो- प्रैट मापक
(घ) बर्गसन - सैमुएलसन सामाजिक कल्याण फलन
IGNOU MEC-01/MEC-101 (July 2023 - January 2024) Assignment Questions
भाग - I
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों का उत्तर दें। प्रत्येक प्रश्न का उत्तर लगभग 700 शब्दों में देना है।
1. क) एक एकाधिकारवादी एक आगत x का उपयोग करता है, जिसे उत्पाद q का उत्पादन करने के लिए निश्चित मूल्य p=5 पर खरीदता है। उसकी मांग और उत्पादन फलन है:
p= 85—3q और q= 2x12 क्रमशः ।
साम्य उत्पादन और साम्य लाभ प्राप्त करें।
ख) "वास्तविक दुनिया में, कभी-कभी इष्टतम कल्याण प्राप्त करना संभव नहीं होता है।" परेटो इष्टतम प्राप्त करने में आने वाली बाधाओं पर टिप्पणी करें और चर्चा करें।
2. निम्नलिखित कॉब- डगलस उपयोगिता फलन पर विचार कीजिए।
U(x,y) = x 1/2 y 1/2
जहाँ x तथा y दो वस्तुएँ हैं, जिनकी प्रति इकाई कीमतें क्रमशः Px और Py पर उपभोग करता है। उपभोक्ता की आय रु M दिये जाने पर निर्धारित कीजिए:
क) वस्तुओं x और y के मार्शलीय माँग फलन ।
ख) उपभोक्ता का अप्रत्यक्ष उपयोगिता फलन ।
ग) α = 1⁄2, Px = रु 2, Py = रु 8 तथा M रु 4000 दिये होने पर उपभोक्ता को प्राप्त अधिकतम उपयोगिता।
घ) रॉय की सर्वसमिका (identity) की व्युत्पत्ति कीजिए।
भाग - II
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों का उत्तर दें। प्रत्येक प्रश्न 12 अंक का है।
3. क) कूर्नो (Cournot) का अल्पाधिकार का मॉडल वर्टेंड ( Bertrand) के अल्पाधिकार के मॉडल से किस प्रकार भिन्न है?
ख) मान लीजिए कि किसी उत्पाद की माँग p=d(q) = -0.8q + 150 और उसी उत्पाद की आपूर्ति p=s(q) = 5.2q द्वारा दी गई है, दोनों फलन के लिए q मात्रा है और p कीमत है। निर्माता अधिशेष और उपभोक्ता अधिशेष ज्ञात कीजिए ।
4. क) सहयोगी एवं असहयोगी खेल सिद्धांत के बीच अंतर करें।
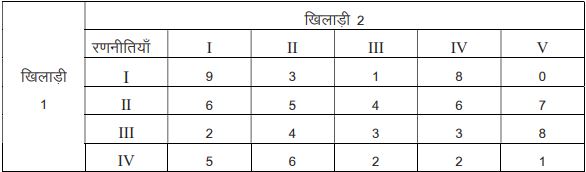
ख) निम्नलिखित प्रतिप्राप्ति आव्यूह (pay off matrix) से निर्धारित करें:
(i) प्रत्येक व्यक्ति के लिए इष्टतम रणनीति ।
ii) खेल का मूल्य
5. क) क्या आप सहमत हैं कि न्यूनतम वेतन से अधिक भुगतान करके नियोक्ता कुशल श्रमिकों को बनाए रख सकते हैं, उत्पादकता बढ़ा सकते हैं, या वफादारी सुनिश्चित कर सकते हैं? दक्षता मजदूरी मॉडल के आलोक में इस कथन पर टिप्पणी कीजिए।
ख) एक उद्योग में दो कंपनियाँ 1 और 2 हैं, प्रत्येक उत्पादक क्रमश: Q1 और Q2 करती हैं और P=50- 2Q द्वारा दी गई उद्योग की मांग का सामना करती हैं, जहाँ P बाजार मूल्य है और Q कुल अर्थात् Q = Q1 +Q2 । मान लें कि लागत फलन C = 10+2q है। ऐसी स्थिति में उद्योग के लिए कूर्नो संतुलन का निर्धारण कीजिए ।
6. क) क्या आपको लगता है कि जोखिम से बचने वाला व्यक्ति जुआ खेलेगा या जोखिम प्रेमी बीमा खरीदेगा? अपना जवाब समझाएं।
ख) राधा के पास 10,000 रुपये की संपत्ति है और 0.002 की संभावना के साथ 3600 रुपये की हानि का सामना कर रही है। वह बीमा सुरक्षा के लिए G रुपये देने और व्यक्तिगत रूप से नुकसान का
जोखिम उठाने के बीच उदासीन है। उपयोगिता फलन U (W) = W 1/2 के अनुसार वह W 0 राशि की कुल संपत्ति का मूल्यांकन करती है। G निर्धारित करें।
7. निम्नलिखित पर संक्षिप्त टिप्पणियाँ लिखिए:
क) विभिन्न प्रकार के मूल्य विभेदन
ख) द्विपक्षीय एकाधिकार
ग) मान की मित्तव्ययीताएँ
घ) संयोजनकारी एवं वियोजनकारी साम्यावस्थाएँ
Buy MEC-01/MEC-101 Assignment 

 5. a) What are the conditions of Pareto optimality?
b) Suppose an investor is concerned about a business choice in which there are three prospects. The probability and returns are given below:
5. a) What are the conditions of Pareto optimality?
b) Suppose an investor is concerned about a business choice in which there are three prospects. The probability and returns are given below:
 What is the expected value of the uncertain investment? What is the variance?
6. a.) Do you agree that by paying higher than the minimum wage, employers can retain skilled workers, increase productivity, or ensure loyalty? Comment on the statement in the light of efficiency wage model.
b.) There are two firms 1 and 2 in an industry, each producing output Q1 and Q2 respectively and facing the industry demand given by P=50-2Q, where P is the market price and Q represents the total industry output, that is Q= Q1 + Q2. Assume that the cost function is C = 10 + 2q. Solve for the Cournot equilibrium in such an industry.
7. Write short notes on following:
a) vNM expected utility theory
b) Slutsky’s theorem
c) Arrow prat measure of risk averseness
d) Bergson-Samuelson Social welfare function
What is the expected value of the uncertain investment? What is the variance?
6. a.) Do you agree that by paying higher than the minimum wage, employers can retain skilled workers, increase productivity, or ensure loyalty? Comment on the statement in the light of efficiency wage model.
b.) There are two firms 1 and 2 in an industry, each producing output Q1 and Q2 respectively and facing the industry demand given by P=50-2Q, where P is the market price and Q represents the total industry output, that is Q= Q1 + Q2. Assume that the cost function is C = 10 + 2q. Solve for the Cournot equilibrium in such an industry.
7. Write short notes on following:
a) vNM expected utility theory
b) Slutsky’s theorem
c) Arrow prat measure of risk averseness
d) Bergson-Samuelson Social welfare function 5. a.) Do you agree that by paying higher than the minimum wage, employers can retain skilled workers, increase productivity, or ensure loyalty? Comment on the statement in the light of efficiency wage model.
b.) There are two firms 1 and 2 in an industry, each producing output Q1 and Q2 respectively and facing the industry demand given by P=50-2Q, where P is the market price and Q represents the total industry output, that is Q= Q1 + Q2. Assume that the cost function is C = 10 + 2q. Solve for the Cournot equilibrium in such an industry.
6. a.) Do you think that a risk-averse individual gamble or will a risk lover purchase insurance? Explain your answer.
b) Radha has assets worth 10,000 rupees and is facing a loss of 3,600 with a probability of 0.002. She is indifferent between paying G rupees for insurance protection and assuming the risk of loss personally. She values total assets of amount w≥0 according to the utility function u (w) = w1/2. Determine G.
7. Write short notes on following:
a) Different types of price discrimination
b) Bilateral monopoly
c) Economies of Scale
d) Pooling and separating equilibrium
5. a.) Do you agree that by paying higher than the minimum wage, employers can retain skilled workers, increase productivity, or ensure loyalty? Comment on the statement in the light of efficiency wage model.
b.) There are two firms 1 and 2 in an industry, each producing output Q1 and Q2 respectively and facing the industry demand given by P=50-2Q, where P is the market price and Q represents the total industry output, that is Q= Q1 + Q2. Assume that the cost function is C = 10 + 2q. Solve for the Cournot equilibrium in such an industry.
6. a.) Do you think that a risk-averse individual gamble or will a risk lover purchase insurance? Explain your answer.
b) Radha has assets worth 10,000 rupees and is facing a loss of 3,600 with a probability of 0.002. She is indifferent between paying G rupees for insurance protection and assuming the risk of loss personally. She values total assets of amount w≥0 according to the utility function u (w) = w1/2. Determine G.
7. Write short notes on following:
a) Different types of price discrimination
b) Bilateral monopoly
c) Economies of Scale
d) Pooling and separating equilibrium 5. (क) पेरोटो इष्टतम की शर्तें क्या हैं?
(ख) माना कि एक निवेशकर्त्ता एक व्यवसाय विकल्प के बारे में चिंतित है, जिसमें तीन संभावनाएँ हैं, प्रायिकता तथा प्रतिफल नीचे दिए गए है:
5. (क) पेरोटो इष्टतम की शर्तें क्या हैं?
(ख) माना कि एक निवेशकर्त्ता एक व्यवसाय विकल्प के बारे में चिंतित है, जिसमें तीन संभावनाएँ हैं, प्रायिकता तथा प्रतिफल नीचे दिए गए है:
 अनिश्चित निवेश का प्रत्याशित मान क्या है? विचरण क्या है?
6. (क) क्या आप सहमत हैं कि न्यूनतम वेतन से अधिक भुगतान करके नियोक्ता कुशल श्रमिकों को बनाए रख सकते हैं, उत्पादकता बढ़ा सकते हैं, या वफादारी सुनिश्चित कर सकते हैं? दक्षता मजदूरी मॉडल के आलोक में कथन पर टिप्पणी कीजिए ।
(ख) एक उद्योग में दो फर्म 1 और 2 हैं, जिनमें से प्रत्येक क्रमशः Q और Q2 आउटपुट का उत्पादन करती है और P= 50-2Q द्वारा दी गई उद्योग मांग का सामना करती है, जहाँ P बाजार मूल्य है और Q कुल उद्योग आउटपुट का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है, जो Q=Q1 + Q2 है। मान लें कि लागत फलन C=10=2q है। ऐसे उद्योग में कूर्नो संतुलन के लिए हल करें।
7. निम्नलिखित पर संक्षिप्त टिप्पणीयाँ लिखिए:
(क) VNM प्रत्याक्षित सिद्धांत
(ख) स्लटस्की प्रमेय
(ग) जोखिम विरति का ऐरो- प्रैट मापक
(घ) बर्गसन - सैमुएलसन सामाजिक कल्याण फलन
अनिश्चित निवेश का प्रत्याशित मान क्या है? विचरण क्या है?
6. (क) क्या आप सहमत हैं कि न्यूनतम वेतन से अधिक भुगतान करके नियोक्ता कुशल श्रमिकों को बनाए रख सकते हैं, उत्पादकता बढ़ा सकते हैं, या वफादारी सुनिश्चित कर सकते हैं? दक्षता मजदूरी मॉडल के आलोक में कथन पर टिप्पणी कीजिए ।
(ख) एक उद्योग में दो फर्म 1 और 2 हैं, जिनमें से प्रत्येक क्रमशः Q और Q2 आउटपुट का उत्पादन करती है और P= 50-2Q द्वारा दी गई उद्योग मांग का सामना करती है, जहाँ P बाजार मूल्य है और Q कुल उद्योग आउटपुट का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है, जो Q=Q1 + Q2 है। मान लें कि लागत फलन C=10=2q है। ऐसे उद्योग में कूर्नो संतुलन के लिए हल करें।
7. निम्नलिखित पर संक्षिप्त टिप्पणीयाँ लिखिए:
(क) VNM प्रत्याक्षित सिद्धांत
(ख) स्लटस्की प्रमेय
(ग) जोखिम विरति का ऐरो- प्रैट मापक
(घ) बर्गसन - सैमुएलसन सामाजिक कल्याण फलन 5. क) क्या आप सहमत हैं कि न्यूनतम वेतन से अधिक भुगतान करके नियोक्ता कुशल श्रमिकों को बनाए रख सकते हैं, उत्पादकता बढ़ा सकते हैं, या वफादारी सुनिश्चित कर सकते हैं? दक्षता मजदूरी मॉडल के आलोक में इस कथन पर टिप्पणी कीजिए।
ख) एक उद्योग में दो कंपनियाँ 1 और 2 हैं, प्रत्येक उत्पादक क्रमश: Q1 और Q2 करती हैं और P=50- 2Q द्वारा दी गई उद्योग की मांग का सामना करती हैं, जहाँ P बाजार मूल्य है और Q कुल अर्थात् Q = Q1 +Q2 । मान लें कि लागत फलन C = 10+2q है। ऐसी स्थिति में उद्योग के लिए कूर्नो संतुलन का निर्धारण कीजिए ।
6. क) क्या आपको लगता है कि जोखिम से बचने वाला व्यक्ति जुआ खेलेगा या जोखिम प्रेमी बीमा खरीदेगा? अपना जवाब समझाएं।
ख) राधा के पास 10,000 रुपये की संपत्ति है और 0.002 की संभावना के साथ 3600 रुपये की हानि का सामना कर रही है। वह बीमा सुरक्षा के लिए G रुपये देने और व्यक्तिगत रूप से नुकसान का
जोखिम उठाने के बीच उदासीन है। उपयोगिता फलन U (W) = W 1/2 के अनुसार वह W 0 राशि की कुल संपत्ति का मूल्यांकन करती है। G निर्धारित करें।
7. निम्नलिखित पर संक्षिप्त टिप्पणियाँ लिखिए:
क) विभिन्न प्रकार के मूल्य विभेदन
ख) द्विपक्षीय एकाधिकार
ग) मान की मित्तव्ययीताएँ
घ) संयोजनकारी एवं वियोजनकारी साम्यावस्थाएँ
5. क) क्या आप सहमत हैं कि न्यूनतम वेतन से अधिक भुगतान करके नियोक्ता कुशल श्रमिकों को बनाए रख सकते हैं, उत्पादकता बढ़ा सकते हैं, या वफादारी सुनिश्चित कर सकते हैं? दक्षता मजदूरी मॉडल के आलोक में इस कथन पर टिप्पणी कीजिए।
ख) एक उद्योग में दो कंपनियाँ 1 और 2 हैं, प्रत्येक उत्पादक क्रमश: Q1 और Q2 करती हैं और P=50- 2Q द्वारा दी गई उद्योग की मांग का सामना करती हैं, जहाँ P बाजार मूल्य है और Q कुल अर्थात् Q = Q1 +Q2 । मान लें कि लागत फलन C = 10+2q है। ऐसी स्थिति में उद्योग के लिए कूर्नो संतुलन का निर्धारण कीजिए ।
6. क) क्या आपको लगता है कि जोखिम से बचने वाला व्यक्ति जुआ खेलेगा या जोखिम प्रेमी बीमा खरीदेगा? अपना जवाब समझाएं।
ख) राधा के पास 10,000 रुपये की संपत्ति है और 0.002 की संभावना के साथ 3600 रुपये की हानि का सामना कर रही है। वह बीमा सुरक्षा के लिए G रुपये देने और व्यक्तिगत रूप से नुकसान का
जोखिम उठाने के बीच उदासीन है। उपयोगिता फलन U (W) = W 1/2 के अनुसार वह W 0 राशि की कुल संपत्ति का मूल्यांकन करती है। G निर्धारित करें।
7. निम्नलिखित पर संक्षिप्त टिप्पणियाँ लिखिए:
क) विभिन्न प्रकार के मूल्य विभेदन
ख) द्विपक्षीय एकाधिकार
ग) मान की मित्तव्ययीताएँ
घ) संयोजनकारी एवं वियोजनकारी साम्यावस्थाएँ