1. Answer in brief:
i) The XeO3 molecule has a trigonal pyramidal structure(like the Ammonia molecule). List its symmetries.
ii) List any two missing planes for the fcc lattice.
iii) What are the advantages of the neutron diffraction method?
iv) Write down the electronic configuration of the Ge atom. What type of bonding would you expect to find in Ge?
v) List the independent elastic constants for a cubic crystal and state their significance.
vi) If a wave function Ψ(x) is to represent an electron in a crystalline solid, what should be its nature?
vii) Write down the energy for the first excited state for electrons in a 3D box. What is the degeneracy of this energy level?
viii) What is the effect of dopant concentration on the Fermi energy and carrier concentration of a p-type semiconductor?
ix) In which of the following ions do you expect angular momentum quenching and why:
Ti 3+, Gd 3+, Ni 2+
x) What is the function of the quartz crystal used in a digital watch?
2. a) A plane intercepts the x-axis at 2a, the y-axis at 3b and the z-axis at 4c. Determine the Miller indices of this plane and the interplanar distance if the lattice parameter is 4.0 Å.
b) A metallic element has an atomic weight of 27 u, density 2710kgm-3 and lattice constant 4.05 Å. Predict its crystal structure and calculate the nearest neighbor distance.
c) The Bragg angle for reflection from the (110) planes in bcc iron is 22º for an x-ray of wavelength 1.54 Å. Find the lattice parameter for iron (take n = 1). What is the minimum wavelength with which the structure of this unit cell can be probed?
d) Show that the reciprocal lattice for a bcc lattice is an fcc lattice.
3. a) The potential energy of a crystal is described by the expression:
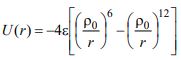
where ε = 3.12x10-3 eV and ρ0 = 2.5Å. Calculate the minimum potential energy.
b) The frequency of the longitudinal optical phonon for NaCl at the centre of the first Brillouin zone is 5rads -1. Calculate the interatomic force constant for this material.
(The atomic weight of Na = 23u and Cl = 37u)
c) Calculate the Debye specific heat of Molybdenum at 300 K, given that its Debye frequency is 9.74 x 10 13 rads -1.
d) The values of the elastic stiffness constants for GaAs are:
C11=1.18 x 10 11 Nm -2, C44 = 0.59 x 10 11 Nm -2 and C12 = 0.54 x 10 11 Nm -2
Given that the density of GaAs is 5.32gcm -3 determine the velocity of the transverse and longitudinal elastic waves in the [100] direction.
4. a) Calculate the transition temperature for a superconductor whose energy gap is 1.65x10-3 eV .
b) For a Si semiconductor, Nc = 2.8x10 19 cm-3 and NV = 1.04x10 19 cm-3. Determine the position of the Fermi level at room temperature for NA = 10 17 cm-3 and ND = 10 14 cm-3.
c) Calculate the Fermi energy and Fermi temperature for potassium metal, whose electron number density is 1.4x10 28 cm-3.
d) When 20 mA of current is passed through a specimen under a magnetic field of 0.5 Wbm-2, the measured Hall voltage is 37μV. If the width of the specimen is 0.01 mm, calculate the Hall coefficient.
5. a) The saturation magnetization of fcc Ni is 5.1 x 10 5 A/ m. If the lattice constant for Ni is 3.52 Å, calculate the net magnetic moment per Ni atom in the crystal in units of Bohr magnetons.
b) What are fusible alloys? Explain their use in safety sprinklers.
c) Explain addition and condensation polymerization with an example of each.
d) Explain, with a diagram, the operation of a photovoltaic solar cell.
1. Answer in brief:
i) List the symmetries of the CH3OH molecule.
ii) Calculate the Miller indices of a crystal plane that intersects the three axes along the basis vectors
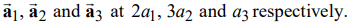
iii) In an
fcc lattice, explain from which of the following plane/planes x-ray diffraction may be observed: (0,2,1), (0,0,1), (0,1,1).
iv) The melting point of potassium is 63.5°C and that of potassium chloride is 770°C. How do you explain this?
v) To study the elastic properties of a cubic crystal we need to determine three elastic stiffness constants, whereas to study the elastic properties of a orthorhombic crystal we need to determine nine elastic stiffness constants. Explain.
vi) What are the shortcomings of the classical theory of heat capacity?
vii) Explain why there is no difference between the electrical conductivity of a semiconductor and an insulator at T =0 K.
viii) Explain what are super electrons and normal electrons in the two fluid model of superconductivity.
ix) Can a LCD display be used in a car? Explain.
x) Can a pyroelectric material be used as a transducer? Explain
2. a) The primitive lattice vectors of a lattice are given by
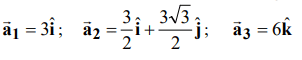
Determine the volume of the primitive cell and the reciprocal lattice vectors.
b) Calculate the atomic packing fraction for the Magnesium crystal.
c) A metallic element has a density of 10.5 g/cm3, a molecular weight of 108.0 u and a lattice constant of 4.09Å. Determine the number of atoms in a unit cell of this element and predict its crystal structure.
d) Determine the first order Bragg reflection angle from the (111) planes in a cubic crystal with lattice constant 4.2 Å for an x-ray beam with
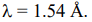
3. a) Calculate the lattice energy per mole of CsCl given that the value of the Madelung constant, repulsive exponent (n) and inter-ionic separation for CsCl are 1.763, 10.7 and 3.5 Å respectively.
b) The elastic stiffness constants for a material are
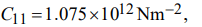
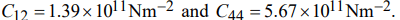
If the density of the material is 3510 kg m-3, calculate the velocity of the longitudinal elastic waves propagating in the [110] direction.
c) The Debye frequency of aluminium is 9.66 X 10 13 Hz. Calculate its molar heat capacity at 10K.
d) In a chain of two different types of atoms show that the group velocity at k = 0 is zero for the optical branch.
4. a) The atomic weight is of a monovalent metal is 197u and it’s density is 19.32g cm-3 . Calculate the density of conduction electrons. Given that the Fermi energy of the metal is 5.53eV calculate the electronic thermal conductivity at 300 K.
b) The effective mass of the electron and hole in Si are 0.26 me and 0.39 me respectively. Calculate the effective density of states in the valence band and conduction band and the intrinsic carrier concentration at 300 K, given that the band-gap is Eg = 1.12 eV.
c) In a Hall experiment, in a silver specimen of width 2.0 cm, the current value is 100 A and the magnetic field is 1.5 T. For a carrier concentration of 6.0 × 10 28 electrons per m3, calculate the Hall voltage.
d) Calculate the limiting value of the magnetic field for which lead will act as a superconductor at 4 K. Take Bac(0) = 80.0 mT and Tc = 8.0 K for lead.
5. a) Determine the magnetic moment of Co2+Fe3+O4.
b) Describe the method used to grow crystals of the compound semiconductor GaAs.
c) Explain addition and condensation polymerization with an example of each.
d) Why are the properties of thin films different from their bulk counterparts? Explain how they are used as interference filters.

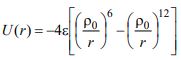 where ε = 3.12x10-3 eV and ρ0 = 2.5Å. Calculate the minimum potential energy.
b) The frequency of the longitudinal optical phonon for NaCl at the centre of the first Brillouin zone is 5rads -1. Calculate the interatomic force constant for this material.
(The atomic weight of Na = 23u and Cl = 37u)
c) Calculate the Debye specific heat of Molybdenum at 300 K, given that its Debye frequency is 9.74 x 10 13 rads -1.
d) The values of the elastic stiffness constants for GaAs are:
C11=1.18 x 10 11 Nm -2, C44 = 0.59 x 10 11 Nm -2 and C12 = 0.54 x 10 11 Nm -2
Given that the density of GaAs is 5.32gcm -3 determine the velocity of the transverse and longitudinal elastic waves in the [100] direction.
4. a) Calculate the transition temperature for a superconductor whose energy gap is 1.65x10-3 eV .
b) For a Si semiconductor, Nc = 2.8x10 19 cm-3 and NV = 1.04x10 19 cm-3. Determine the position of the Fermi level at room temperature for NA = 10 17 cm-3 and ND = 10 14 cm-3.
c) Calculate the Fermi energy and Fermi temperature for potassium metal, whose electron number density is 1.4x10 28 cm-3.
d) When 20 mA of current is passed through a specimen under a magnetic field of 0.5 Wbm-2, the measured Hall voltage is 37μV. If the width of the specimen is 0.01 mm, calculate the Hall coefficient.
5. a) The saturation magnetization of fcc Ni is 5.1 x 10 5 A/ m. If the lattice constant for Ni is 3.52 Å, calculate the net magnetic moment per Ni atom in the crystal in units of Bohr magnetons.
b) What are fusible alloys? Explain their use in safety sprinklers.
c) Explain addition and condensation polymerization with an example of each.
d) Explain, with a diagram, the operation of a photovoltaic solar cell.
where ε = 3.12x10-3 eV and ρ0 = 2.5Å. Calculate the minimum potential energy.
b) The frequency of the longitudinal optical phonon for NaCl at the centre of the first Brillouin zone is 5rads -1. Calculate the interatomic force constant for this material.
(The atomic weight of Na = 23u and Cl = 37u)
c) Calculate the Debye specific heat of Molybdenum at 300 K, given that its Debye frequency is 9.74 x 10 13 rads -1.
d) The values of the elastic stiffness constants for GaAs are:
C11=1.18 x 10 11 Nm -2, C44 = 0.59 x 10 11 Nm -2 and C12 = 0.54 x 10 11 Nm -2
Given that the density of GaAs is 5.32gcm -3 determine the velocity of the transverse and longitudinal elastic waves in the [100] direction.
4. a) Calculate the transition temperature for a superconductor whose energy gap is 1.65x10-3 eV .
b) For a Si semiconductor, Nc = 2.8x10 19 cm-3 and NV = 1.04x10 19 cm-3. Determine the position of the Fermi level at room temperature for NA = 10 17 cm-3 and ND = 10 14 cm-3.
c) Calculate the Fermi energy and Fermi temperature for potassium metal, whose electron number density is 1.4x10 28 cm-3.
d) When 20 mA of current is passed through a specimen under a magnetic field of 0.5 Wbm-2, the measured Hall voltage is 37μV. If the width of the specimen is 0.01 mm, calculate the Hall coefficient.
5. a) The saturation magnetization of fcc Ni is 5.1 x 10 5 A/ m. If the lattice constant for Ni is 3.52 Å, calculate the net magnetic moment per Ni atom in the crystal in units of Bohr magnetons.
b) What are fusible alloys? Explain their use in safety sprinklers.
c) Explain addition and condensation polymerization with an example of each.
d) Explain, with a diagram, the operation of a photovoltaic solar cell.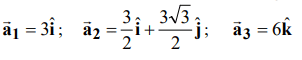 Determine the volume of the primitive cell and the reciprocal lattice vectors.
b) Calculate the atomic packing fraction for the Magnesium crystal.
c) A metallic element has a density of 10.5 g/cm3, a molecular weight of 108.0 u and a lattice constant of 4.09Å. Determine the number of atoms in a unit cell of this element and predict its crystal structure.
d) Determine the first order Bragg reflection angle from the (111) planes in a cubic crystal with lattice constant 4.2 Å for an x-ray beam with
Determine the volume of the primitive cell and the reciprocal lattice vectors.
b) Calculate the atomic packing fraction for the Magnesium crystal.
c) A metallic element has a density of 10.5 g/cm3, a molecular weight of 108.0 u and a lattice constant of 4.09Å. Determine the number of atoms in a unit cell of this element and predict its crystal structure.
d) Determine the first order Bragg reflection angle from the (111) planes in a cubic crystal with lattice constant 4.2 Å for an x-ray beam with