Bought By: 7843
Rating: 4.5

Get Good Marks in your B.Sc. Chemistry Programme in the Term-End Exams even if you are busy in your job or profession.
We've sold over 39,293,435 Help Books and Delivered 47,786,434 Assignments Since 2002.
As our customers will tell you...yes, it really result-oriented.
 8. a) The rate constant for Cr decay is 2.89×10−7 s−1. Calculate the time required for 87.5% decay.
b) Explain the method of determining the age of an organic material.
c) Explain the following terms:
i) Moderator and
ii) Breeder reactor.
9. a) Among the molecules given below, identify those which are microwave active.
Br2, HF, CO2 and CO
b) Write down the values of two characteristic frequencies for each of the following compounds:
8. a) The rate constant for Cr decay is 2.89×10−7 s−1. Calculate the time required for 87.5% decay.
b) Explain the method of determining the age of an organic material.
c) Explain the following terms:
i) Moderator and
ii) Breeder reactor.
9. a) Among the molecules given below, identify those which are microwave active.
Br2, HF, CO2 and CO
b) Write down the values of two characteristic frequencies for each of the following compounds:
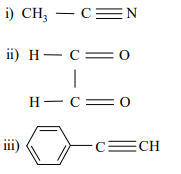 c) State the condition to be satisfied for a molecule to absorb in the microwave region.
10. a) Give an example for each of the following types of nuclear transmutation reactions:
( p, α), ( n, p), ( n, α) and ( p, n)
b) An analyst is asked to oxidize a secondary alcohol to ketone. What single characteristic feature in IR spectra should the analyst look for in order to verify the feasibility of the reaction?
c) Which of the following has higher λmax value?
1-butene or 1, 3 – butadiene.
State the reason.
d) Calculate the molar diamagnetic susceptibility value of acetophenone.
c) State the condition to be satisfied for a molecule to absorb in the microwave region.
10. a) Give an example for each of the following types of nuclear transmutation reactions:
( p, α), ( n, p), ( n, α) and ( p, n)
b) An analyst is asked to oxidize a secondary alcohol to ketone. What single characteristic feature in IR spectra should the analyst look for in order to verify the feasibility of the reaction?
c) Which of the following has higher λmax value?
1-butene or 1, 3 – butadiene.
State the reason.
d) Calculate the molar diamagnetic susceptibility value of acetophenone.To attend IGNOU CHE-01 Term-End Examination, you must first submit your Assignments to the university and it is possible from the CHE-01 study material. You can solve all necessary Assignments using Help Books. This will help in gaining good marks.
All best wishes with our efforts that you do not meet any obstacle before attending examinations next year. You can pass the B.Sc. Chemistry Programme Annual Exams with a good grade using Books/Materials from any one place at home or anywhere else!
ALL THE BEST!!!
Team GullyBaba